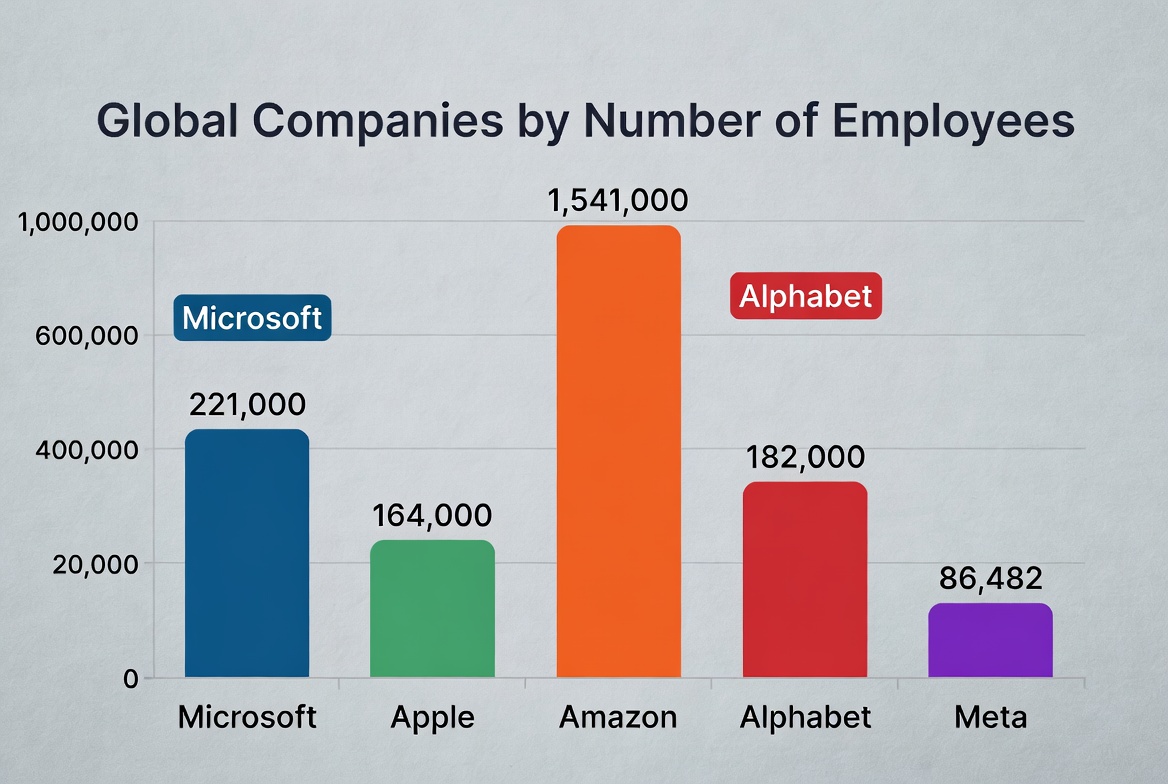
Top 10 countries by share of female entrepreneurship
We benchmark women-led entrepreneurship using internationally comparable indicators (GEM TEA for women and government reporting on women-owned SMEs), then summarize flagship public programs that expand access to capital, markets, and training.
Why this matters
Women-owned firms lift household incomes, diversify supply chains, и help economies absorb shocks. The World Bank, OECD and UN agencies consistently link female entrepreneurship with higher employment elasticity in services and local commerce—especially when credit constraints and legal barriers are addressed.
Indicators used: (1) GEM TEA (female) — share of adult women engaged in early-stage entrepreneurship; (2) government/IFIs’ reporting on women-owned SMEs; (3) legal and finance enablers from Women, Business and the Law and OECD work on inclusive SMEs. Figures vary by year; we present a stable cross-section and the most consequential public programs in each economy.
Methodology & caveats
- Ranking lens: Countries are ordered by high female TEA rates observed in recent GEM waves and corroborated with official briefs on women-owned SMEs.
- Comparability: TEA captures early-stage activity (nascent + new business owners) and can exceed the share of women among employer firms; both lenses are relevant for inclusion policy.
- Uncertainty: Small rank shifts occur across years; consult linked sources for the latest economy profiles.
All sources are multilateral/official (World Bank/IFC, OECD, ILOSTAT, UN Women, GEM). Links below.
Female Entrepreneurship — Leaders & Flagship Public Programs
Countries with high female early-stage entrepreneurship (GEM TEA, women) and robust government support. Numbering (1–10) applies only to countries; programs are bulleted.
-
Angola
High female TEA in recent GEM waves; strong opportunity-driven microenterprise base.
- INAPEM — national MSME agency: training, certification and advisory for women-led SMEs.
- PRODESI — economic diversification with grant/credit windows and women participation tracks.
-
Botswana
Among Africa’s leaders in female TEA; formalization improving via citizen-enterprise schemes.
- CEDA — concessional loans with youth/women products.
- LEA (Local Enterprise Authority) — incubation and export-readiness for women MSMEs.
-
Uganda
Very high women’s startup activity across retail and agro value chains.
- UWEP — Uganda Women Entrepreneurship Programme (group grants/loans + skills).
- Parish Development Model — production & marketing support with women quotas.
-
Ghana
Large share of women in services/retail startups; onboarding into formality accelerating.
- Ghana Enterprise Agency (GEA) — Women Entrepreneurship initiatives and SME finance.
- MASLOC — micro-loans prioritizing women-owned microenterprises.
-
Nigeria
Big base of women founders; growth in fintech and creative industries.
- Bank of Industry — Gender Business Initiative (dedicated credit lines and advisory).
- GEEP (Trader/MarketMoni) — micro-credit with high female uptake.
-
Saudi Arabia
Female entrepreneurship surged with legal reforms under Vision 2030.
- Monsha’at — SME Authority programs for training, acceleration and market access.
- Kafalah — government loan guarantees accessible to women-owned SMEs.
-
United Arab Emirates
High female TEA and growing women-owned employer firms in services and e-commerce.
- Khalifa Fund & Dubai SME — financing plus mentorship/advisory for women founders.
- UAE Gender Balance Council — policy coordination, incl. entrepreneurship initiatives.
-
Colombia
Robust pipeline of women-led startups; strong services/export orientation.
- iNNpulsa & SENA/Fondo Emprender — seed grants and acceleration for women.
- Bancóldex — dedicated credit lines for women-owned SMEs (state development bank).
-
Chile
Female TEA above regional average; steady formalization of micro and small enterprises.
- SERCOTEC — Capital Abeja — competitive grants exclusively for women.
- CORFO — co-investment and acceleration programs with women tracks.
-
Panama
Female TEA above the LatAm average; niches in logistics and commerce.
- AMPYME — Mujer Emprendedora — seed grants and training.
- INADEH — skills programs oriented to women-led SMEs.
Also notable: Canada — Women Entrepreneurship Strategy (WES); Philippines — DTI Negosyo Centers & SB Corp women financing; Rwanda — BDF Women Guarantee.
Female Early-Stage Entrepreneurship (TEA) — Indicative Top-10
Values are rounded and indicative, aligned with ranges seen in recent GEM economy profiles. Axis 0–50%.
Primary Intergovernmental / Government Sources
- Global Entrepreneurship Monitor (GEM) — Economy Profiles & Women’s Entrepreneurship reports
- World Bank — Women, Business and the Law (legal enablers)
- IFC/World Bank — Women Entrepreneurs Finance Initiative & SME Finance
- ILOSTAT — Female employers & self-employment indicators
- OECD — Inclusive Entrepreneurship & Women-owned SMEs
- UN Women — policy trackers & procurement for women-owned businesses
Programs named above are official national schemes (SME agencies, development banks, or cabinet-level initiatives). Always check the latest eligibility and budget windows before citing figures.